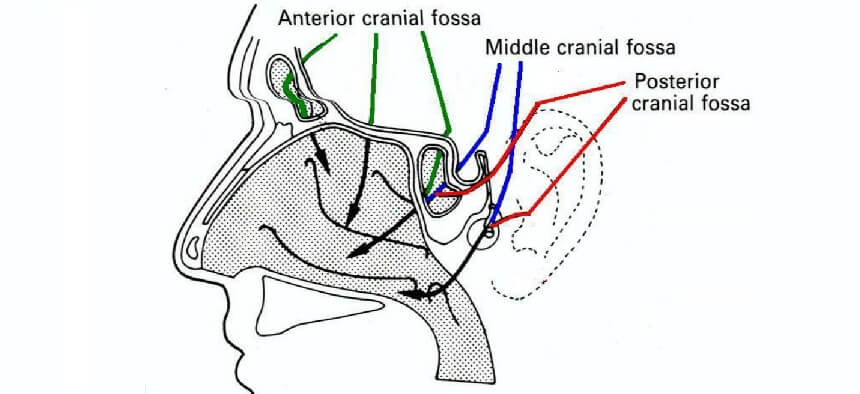
A cerebrospinal fluid leak is a condition in which the protective fluid surrounding the brain – the CSF – leaks into the sinuses or the ears. Normally the brain is a sterile compartment that is separated from the sinuses and the ears by a bony separation called the skull base. CSF surrounds the brain and cushions it. A thick, leathery tissue called dura lines the inside of the skull, providing a seal that prevents spinal fluid from escaping. CSF leaks occur when there is a breakdown in this barrier. The dura can be damaged by certain surgeries, head trauma, and tumors. Leaks sometimes occur spontaneously. Untreated CSF leaks can lead to life-threatening meningitis, brain infections, or stroke.
Symptoms :
Symptoms of a CSF leak typically include:
- * A headache that worsens upon sitting up and eases upon lying down.
- * Clear drainage from the ear (CSF otorrhea) or the nose (CSF rhinorrhea) when leaning forward or straining